Education
How does Crypto token supply affect price?

As cryptocurrencies and digital assets continue to grow in popularity and mainstream adoption, it’s important to understand the various factors that can influence the value of these assets. One such factor is the supply of tokens, which can have a significant impact on their price.
In this article, we will explore the relationship between token supply and price, and how different supply scenarios can affect the value of a token. We will also discuss the concept of “market cap” and how it relates to token supply and price. By the end of this article, you will have a deeper understanding of how token supply can affect the value of a digital asset.
Crypto token supply and price, are vital factors that can influence the price of a cryptocurrency or digital asset. But to understand how this influence happens, we first need to understand what tokenomics means.
Tokenomics is the study of the economic and financial aspects of cryptocurrencies and digital assets, to provide valuable insights into the relationship between token supply and price. But what we must understand is that the relationship between token supply and price is complex and multifaceted, and it’s not always easy to predict how changes in token supply will affect the price of a given asset.
In order to fully understand this relationship, it’s important to consider a variety of factors that may influence the supply and demand for a given asset, as well as the broader context in which it is being traded. To begin with, it’s important to understand that token supply is just one factor that can influence the price of a cryptocurrency or digital asset. There are many other factors that can also affect the price, including market sentiment, regulatory developments, technological innovations, and more.
To understand how token supply can affect price, it’s important to first understand the concept of supply and demand. In economics, supply refers to the amount of a particular good or service that is available for purchase, while demand refers to the desire or willingness of consumers to buy that good or service. When there is a high demand for a product and a limited supply, the price of that product will tend to increase. On the other hand, when there is a large supply of a product and a low demand for it, the price will tend to decrease.
This basic principle of economics can also be applied to the market for cryptocurrencies and digital assets. When there is a high demand for a particular cryptocurrency and a limited supply of it, the price of that cryptocurrency will tend to increase. Conversely, when there is a large supply of cryptocurrency and a low demand for it, the price will tend to decrease.
Another way to further explore the relationship between token supply and price is to use statistical analysis to quantify the strength and direction of the relationship. For example, we could use regression analysis to determine the degree to which changes in token supply are associated with changes in price.
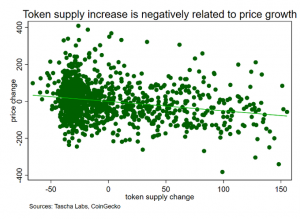
One way to begin analyzing the data is to plot the market capitalization of each token against the total supply of that token. Now, analyzing data from the top 718 tokens by market capitalization (not fully diluted) over the past two years, we can visualize the relationship between these two variables and identify any patterns or trends that may emerge.
Upon examining the data, we can see that there is a wide range of values for both market capitalization and total supply among the top 718 tokens. Some tokens have very high market capitalizations and relatively low total supplies, while others have lower market capitalizations and much larger total supplies.
At first glance, it may seem that there is no clear relationship between token supply and price. However, upon closer examination, we can see that there does appear to be some correlation between these two variables. In general, tokens with lower total supplies tend to have higher market capitalizations, while tokens with higher total supplies tend to have lower market capitalizations. This suggests that token supply may indeed affect price to some extent.
Another way to examine the relationship between token supply and price is to look at the concept of “market capitalization.” Market capitalization, or “market cap,” is a measure of the total value of a cryptocurrency or digital asset. It is calculated by multiplying the asset’s current price by the total number of units of the asset in circulation.
By analyzing the market capitalization of a particular asset over time, we can get a sense of how changes in token supply have affected the price of the asset. For example, if the market capitalization of an asset increases while the total supply remains constant, this may indicate that the demand for the asset has increased and the price has gone up. On the other hand, if the market capitalization decreases while the total supply remains constant, this may indicate that the demand for the asset has decreased and the price has gone down.
Now, let’s look at a vivid example. Let’s assume that a particular cryptocurrency has a market cap of $100 million and there are 10 million units of the cryptocurrency in circulation, the price of each unit would be $10. If the supply of the cryptocurrency were to increase to 20 million units while the market cap remained at $100 million, the price of each unit would drop to $5. Conversely, if the supply were to decrease to 5 million units while the market cap remained at $100 million, the price of each unit would increase to $20.
This example illustrates how changes in token supply can affect the price of a cryptocurrency or digital asset. However, it’s important to note that the relationship between token supply and price is not always linear or predictable. There are many other factors that can also influence the price of a cryptocurrency or digital asset, and the impact of any given factor can vary widely depending on the specific circumstances of the asset.
In addition to analyzing market capitalization, it’s also important to consider other factors that may influence the supply and demand for a particular asset. For example, the “tokenomics” of an asset can play a role in shaping its supply and demand. This can include the distribution of the token, the incentives for holding and using the token, and the overall utility of the token in the ecosystem.
For example, if a particular token has a limited supply and strong demand for its use within a particular ecosystem, this may lead to an increase in the price of the token. On the other hand, if a token has a large supply and little demand for its use within a particular ecosystem, this may lead to a decrease in the price of the token.
However, it’s important to note that this relationship is not necessarily linear or predictable. There are many other factors that can also influence the price of a cryptocurrency or digital asset, and the impact of any given factor can vary widely depending on the specific circumstances of the asset.
Conclusion
So, does token supply affect price? It’s difficult to say for certain, as the relationship between token supply and price is complex. However, it is generally accepted that token supply can have an impact on the price of a cryptocurrency or digital asset, although the strength and direction of that impact can vary widely. So, by further examining the market capitalization of an asset and considering the broader context of its tokenomics and other factors that may influence supply and demand, we can always gain a better understanding of the relationship between token supply and price.

























5 Comments